News
New TECH Report - LLDPE (2024 Program)

LLDPE is one in a series of reports published as part of NexantECA’s 2024 Technoeconomics – Energy & Chemicals (TECH) program.
Overview
Linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) is one of a number of polyolefins that are commodity plastics, which are used globally in a wide range of market segments including packaging, consumer, agriculture, and general industrial. LLDPE is produced from ethylene and a comonomer, typically butene-1, hexene-1, or octene-1.
This TECH report provides an updated overview of the technological, economic, and market aspects for LLDPE, including conventional and second generation resins. The following issues are addressed in this report:
- What are the major technologies for LLDPE production and how do they differ? Which ones can also produce HDPE? Which technologies are available for license?
- What comonomers are used and how does it affect the cost of production? How do the process economics compare across processes and different geographic regions?
- How does carbon intensity change for the different technologies explored for LLDPE production?
- What steps are being taken to improve the sustainability of LLDPE production?
Commercial Technologies
The major commercial routes for the production of LLDPE are gas phase, solution, and slurry/slurry loop. Many are swing processes that can also produce HDPE. The technologies are very mature, with licensors focusing on cost reduction, catalyst development, and product enhancement to differentiate their technologies. The scale of most processes has increased significantly, reducing operating and investment costs. Product enhancement efforts focus on improving the properties of LLDPE by itself and as a substitute for LDPE.
Technologies developed by Borealis (BORCEED and BORSTAR), Chevron Phillips (MarTECH), Dow (DOWLEX), INEOS (INNOVENE G), LyondellBasell (SPHERILENE S), Mitsui (EVOLUE), NOVA (SCLAIRTECH and Advanced SCLAIRTECH), and Univation (UNIPOL) are described and analyzed, with a focus on recent developments. A list of licensees is included for each technology.
Process Economics
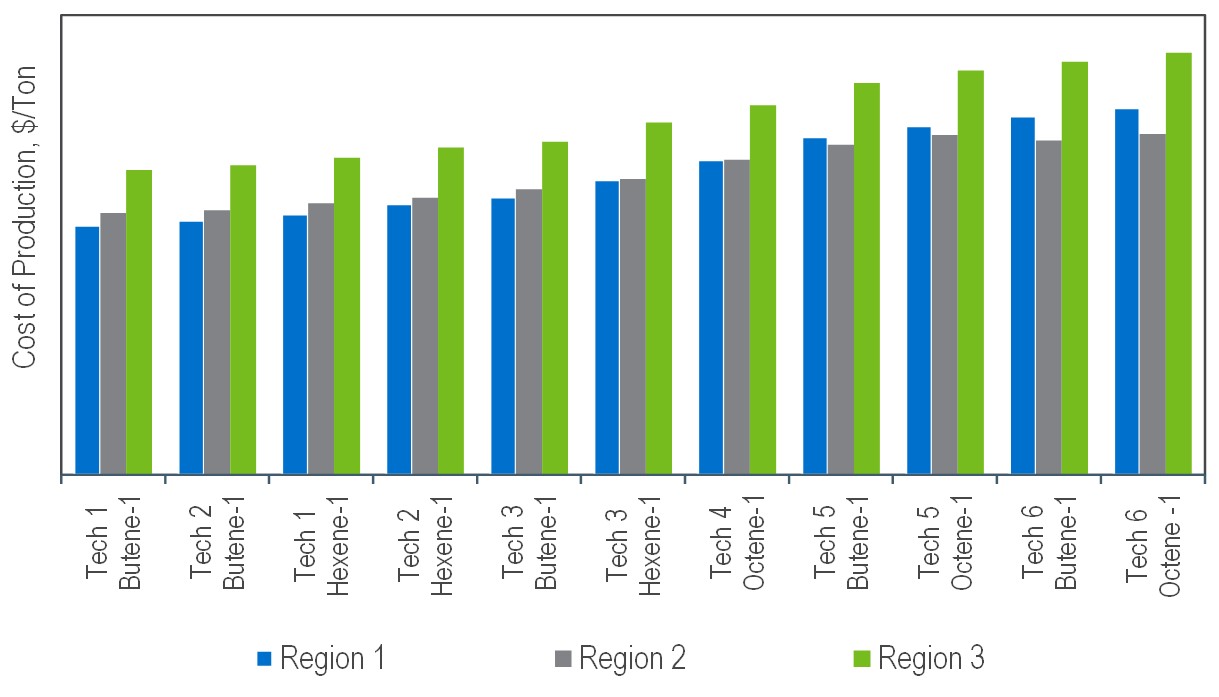
Detailed cost of production estimates for various commercial LLDPE technologies are presented for USGC, coastal China, and Middle East locations using market-priced ethylene. Estimates are developed for conventional, metallocene/single-site, and easy processing film grade resins, depending on the technology. In each region, the comonomer (butene-1, hexene-1, or octene-1) and the technology employed affected the relative cost of production.
Regional Cost of Production Comparison for Conventional LLDPE Resins
Commercial Overview
Global LLDPE consumption was 41.7 million tons in 2023. Film applications are the largest end-use, followed by injection molding, rotomolding, and extrusion. New developments with the aim to improve the sustainability of LLDPE is also included, evaluating routes from low CI crackers to alternative feedstocks, with breakdown by company. A breakdown of capacity by producer for LLDPE on a global and regional basis is provided in this TECH report.
Contact a member to our Insights & Analytics team to find out more about this report
About Us - NexantECA, the Energy and Chemicals Advisory company is the leading advisor to the energy, refining, and chemical industries. Our clientele ranges from major oil and chemical companies, governments, investors, and financial institutions to regulators, development agencies, and law firms. Using a combination of business and technical expertise, with deep and broad understanding of markets, technologies and economics, NexantECA provides solutions that our clients have relied upon for over 50 years.