Blogs
March 03, 2025Exploring the hydrogen colour spectrum: Is blue hydrogen the path to a cleaner future?

Hydrogen, the most abundant element in the universe has emerged as a key player in the transition to a low-carbon future. Hydrogen is a colourless, odourless, tasteless, and highly flammable substance. As governments and industries strive to meet the Paris Climate Agreement's 'net-zero' targets by 2050, the production method of hydrogen becomes critical. While hydrogen itself produces no carbon emissions when used as fuel, the environmental footprint of its production varies significantly.
Liquid hydrogen is utilized in very large volumes in the space program as a primary rocket fuel for combustion with oxygen or fluorine, and as a propellent for nuclear powered rockets and space vehicles. In addition to being a clean-burning fuel, hydrogen can be used as an energy carrier, especially for hard-to-decarbonize sectors like heavy transport and industrial processes. Hydrogen fuel cells offer long-range and quick re-fueling options for trucks and trains, while also being a critical feedstock in industries like chemicals and metallurgy.
The Colour Spectrum of Hydrogen
Despite hydrogen's clean-burning properties, not all hydrogen is created equal. The way it is produced significantly affects its environmental footprint. Enter the hydrogen colour spectrum.
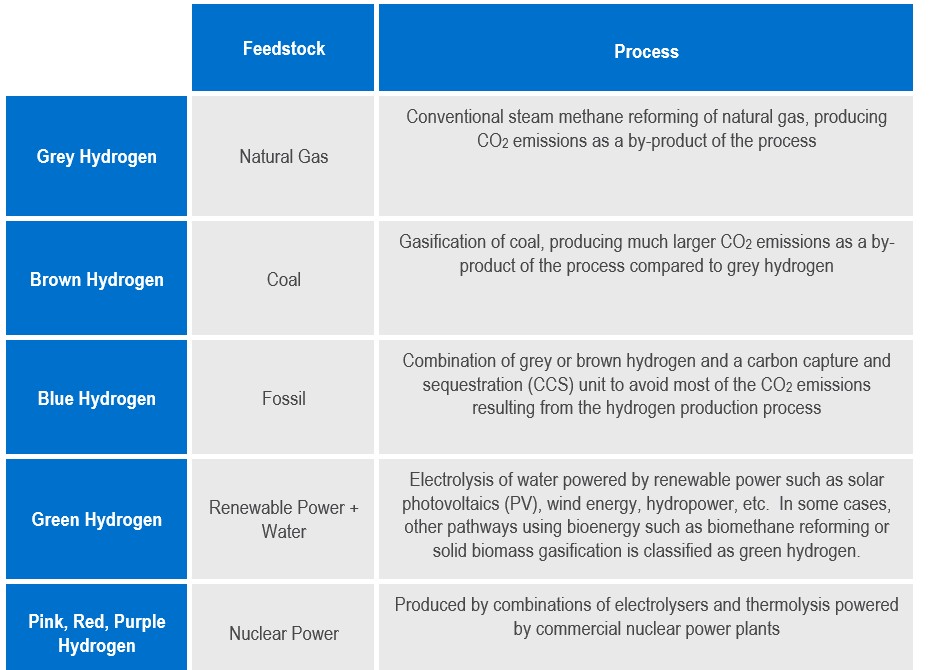
Different types of hydrogen are defined based on a colour palette classifying hydrogen based on its potential environmental footprint and resulting impact. Traditionally, hydrogen has been generated from fossil feedstock using technology that emit significant amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gas (GHGs). Depending on the fossil feedstock, hydrogen produced using conventional fossil pathways are labelled as grey (natural gas) or brown/black (coal) hydrogen. Therefore, despite hydrogen being a clean burning fuel, its production by conventional means can contribute to relatively large CO2 emissions as well as releasing fugitive methane emissions into the atmosphere.
Besides grey and brown, the colour palette of hydrogen includes blue, green, yellow and even pink, red, and purple hydrogen. Most of these colours of hydrogen are produced using relatively novel methods of production such as electrolysis powered by renewable energy (green), a mix of renewable energies and fossil feedstock (yellow), and nuclear power-based hydrogen (pink, red, and purple) which results in no GHG emissions.
Terminology for Hydrogen Technologies
Blue hydrogen takes the conventional process of hydrogen production from inexpensive fossil feedstock but includes a carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) unit which captures the CO2 emissions, preventing the release of CO2 into the atmosphere. The blue hydrogen pathway is able to take advantage of the low cost of production using conventional feedstock with proven technologies, but without the large CO2 emissions associated with using fossil feedstock. The CO2 reduction impact is especially larger when applied to hydrogen production through the coal gasification process.
Why Blue Hydrogen?
Newer processes such as green hydrogen require a large up-front CAPEX investment for equipment such as an electrolyzer, and although hydrogen production using nuclear power uses proven technology and processes, past nuclear power generation incidents has created a negative public perception and presents a key barrier to advancements for this pathway.
While green hydrogen produced from renewable energy is the ideal long-term solution, its high capital costs and reliance on intermittent renewable energy sources make it less viable for widespread adoption today. In contrast, blue hydrogen offers a bridge — allowing hydrogen production using existing fossil infrastructure while significantly reducing emissions through CCS. The figure below shows a simplified flow diagram to produce blue hydrogen:
Fossil Feedstock Route to Blue Hydrogen
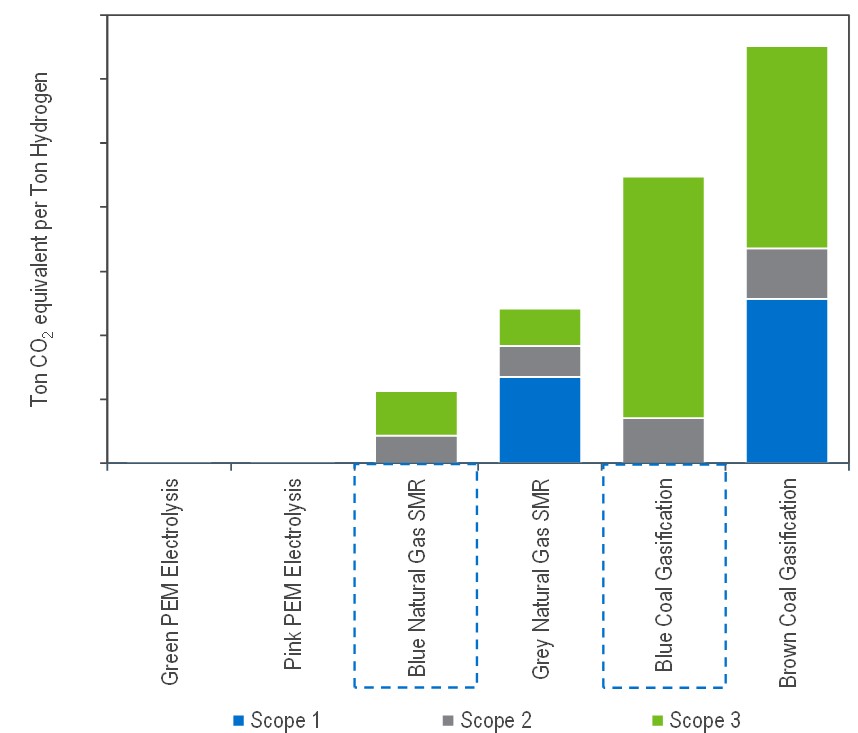
Though retrofitting conventional hydrogen production facilities with CCS units involves upfront capital expenditure (CAPEX), these costs can potentially be mitigated through revenues from CO₂ sales, particularly in industries like enhanced oil recovery (EOR). Additionally, as carbon pricing mechanisms become more widespread, blue hydrogen's lower emissions could lead to significant savings by avoiding hefty carbon taxes. Comparing the carbon intensities of hydrogen production across its colour spectrum, green and pink hydrogen is very nearly carbon neutral due to the carbon neutral nature of its raw materials. However, blue hydrogen is able to reduce carbon intensity of the conventional grey/brown hydrogen production process by around 40 to 50 percent.
Comparative Carbon Intensities of Hydrogen Production
Source NexantECA
Summary and Conclusion...
Blue hydrogen provides a critical stepping stone in the journey towards decarbonization, offering a viable pathway to reduce emissions in the near term while we work to scale up green hydrogen technologies. Hydrogen production is expected evolve from conventional heavily polluting gas and coal-based processes to cleaner alternatives such as blue and green hydrogen. This is supported by the rapidly growing downstream demand for greener fertilizers (ammonia/urea) and fuels. Global hydrogen demand is expected to more than triple by 2050, leaving a gap to be filled by cleaner hydrogen. As the world races to meet its climate goals, the adoption of blue hydrogen is expected to be a relatively cheap method of extending the lifespan of conventional hydrogen facilities in a way that allows hydrogen to be produced using the same fossil feedstock, but with lower emissions. Blue hydrogen can bridge the gap between today's carbon-intensive processes and the cleaner, greener solutions of tomorrow.
The Author...
Ian Lee, Senior Analyst
About Us - NexantECA, the Energy and Chemicals Advisory company is the leading advisor to the energy, refining, and chemical industries. Our clientele ranges from major oil and chemical companies, governments, investors, and financial institutions to regulators, development agencies, and law firms. Using a combination of business and technical expertise, with deep and broad understanding of markets, technologies, and economics, NexantECA provides solutions that our clients have relied upon for over 50 years.