New TECH Report - Decarbonizing Portland Cement (2024 Program)
Decarbonizing Portland Cement is one in a series of reports published as part of NexantECA’s 2024 Technoeconomics – Energy & Chemicals (TECH) program.
Overview
Currently, virtually all cement worldwide is manufactured using widely available, standardized processes that integrate the production of clinker and the combination of clinker with additional solids to produce cement. The cement industry alone is responsible for around five percent of carbon emissions worldwide. The majority of these emissions are caused by fuel consumption and the calcination process.
In recent years, growing regulatory environment in favor of lower carbon emissions has led to increased exploration of carbon intensity reduction routes for cement, As a result of net-zero target timelines drawing near project developers and producers are beginning to pilot and implement carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies for cement applications.
This TECH report covers both commercial and developing technologies for producing Ordinary Portland Cement and addresses questions such as:
What processes are currently employed for clinker and cement production?
What are the potential routes for reducing carbon emissions from the cement industry?
What new developments in CCS have emerged for producing cement with reduced carbon intensity?
How does cost and carbon intensity change for the different methods of producing cement?
Commercial Technologies
The majority of cement is currently produced from limestone via a clinker intermediate. Most manufacturing of Portland cement uses two major process operations, a calciner for clinker production and a grinder to form finished cement. Initially limestone and other raw materials are crushed and ground finely in a raw mill before preheating and precalcination. Raw materials are then converted to clinker in a kiln where high temperature burning of a mix of raw materials to achieve the desired chemical and mineral properties. Cooled clinker is then blended with gypsum and water to form cement.
Process Economics
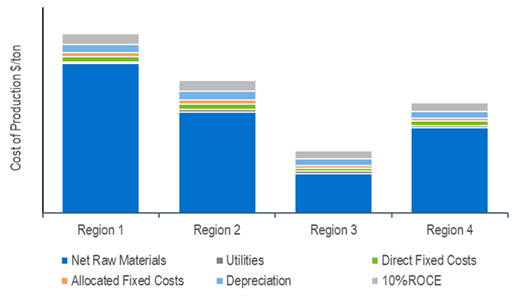
Detailed cost of production estimates for various technologies are presented for the United States, Western Europe, China and South-East Asia locations. Estimates are developed for a cement complex and for CCS technologies.
Cost of Production Comparison for Cement Production
Cost of Production Comparison for Cement Production
Commercial Overview
Cement is a fundamental material in the construction industry, serving as the primary binder in concrete, which is essential for building infrastructure.
The global cement market is driven by rapid urbanization, industrialization, and the increasing demand for residential, commercial, and infrastructure projects. By 2030 production of cement is estimated to be 4.8 billion tons per year.
The industry faces challenges such as environmental regulations and the need for sustainable practices, leading to a growing focus on green cement and alternative materials. Despite these challenges, the cement market continues to expand, particularly in emerging economies where construction activities are booming.
Contact a member to our Insights & Analytics team to find out more about this report