Direct Air Capture (DAC): Capturing value or all hot air?

Driven by commitments to reduce carbon emissions, direct air capture (DAC) technology is being seen by many in the industry as essential in achieving net zero goals, causing many in the industry to contemplate engagement and investment. DAC is a carbon dioxide capture approach that involves removing CO2 directly from the atmosphere to reduce atmospheric CO2 concentration levels and offset CO2 emissions from difficult to decarbonize sectors. The technology has received increasing attention in recent years due to global decarbonization efforts and net zero targets, as well as policy frameworks and corporate sector investment supporting the technology. While it is currently hampered by its large energy requirements and high costs, interest remains high for a few well joined premises:
We are limited by available renewable and sustainable materials and technologies: Simply put, there isn’t enough renewable feedstocks, renewable power, or renewable technologies available between now and 2050 to eliminate the use or impact of fossil fuels. Even at very impressive industry growth rates—in excess of any previous industrial revolution—we will still likely fall short. Many will need a way to offset otherwise uncapturable or ineliminable emissions;
Industry is expecting emissions regulation—and support for emission reduction technologies: Almost all major global multinational energy and chemical companies have publicly stated that they not only expect a carbon tax, cap and trade, and/or some other credit system to help curb emissions in major markets, but that they also support these efforts. DAC, for example, is also a potential recipient of various supports under the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA);
Consequences are stacking for inaction: It is now widely accepted that the global community will miss the target of 1.5 degrees—more powerful storms, raging fires, rising sea levels, droughts, and other disruptions to global food, chemical, and energy industries are rising with the mean temperature of the planet.
View the table of content for Direct Air Capture Technologies (2023) report
While still in its early developmental stages, solid sorbent and liquid solvent DAC approaches are currently furthest along in development compared to other approaches. Typically, hydroxides and amines are used to separate CO2 from incoming ambient air, either introduced as functional groups attached to the surface of a solid material (sorbent DAC) or as aqueous solutions (liquid solvent DAC). The CO2 is then released as a concentrated stream and the sorbent/solvent is regenerated through the application of heat, or other energy input. The main technology challenges faced by DAC, contributing to its current high cost and high energy demands, are primarily due to:
Difficulty of separating the low concentration of CO2 (~400 ppm) in the air
Energy requirements associated with processing large volumes of air
Challenge of achieving a low pressure drop across the air contactor unit
Tradeoff between achieving strong sorbent/solvent interactions with CO2 to capture it from air while minimizing energy requirements to release the CO2
NexantECA has authored the TECH report Direct Air Capture Technologies (2023 Program) on this subject. It provides an overview of DAC technology and economics, as well as market aspects and climate landscape in terms of key policies and project status. More specifically, the report covers:
DAC technology overview, including process descriptions, key challenges and limitations, advantages and disadvantages, and areas for cost-reducing innovation
Detailed review of sorbent- and solvent-based DAC approaches, with a minor focus on other developmental DAC methods such as moisture/humidity swing adsorption, cryogenic, electrochemical/electro-swing adsorption, and membrane-based DAC technologies
Key players and technology holders/licensors of DAC technology as well as an overview of pre-commercial DAC technology developers
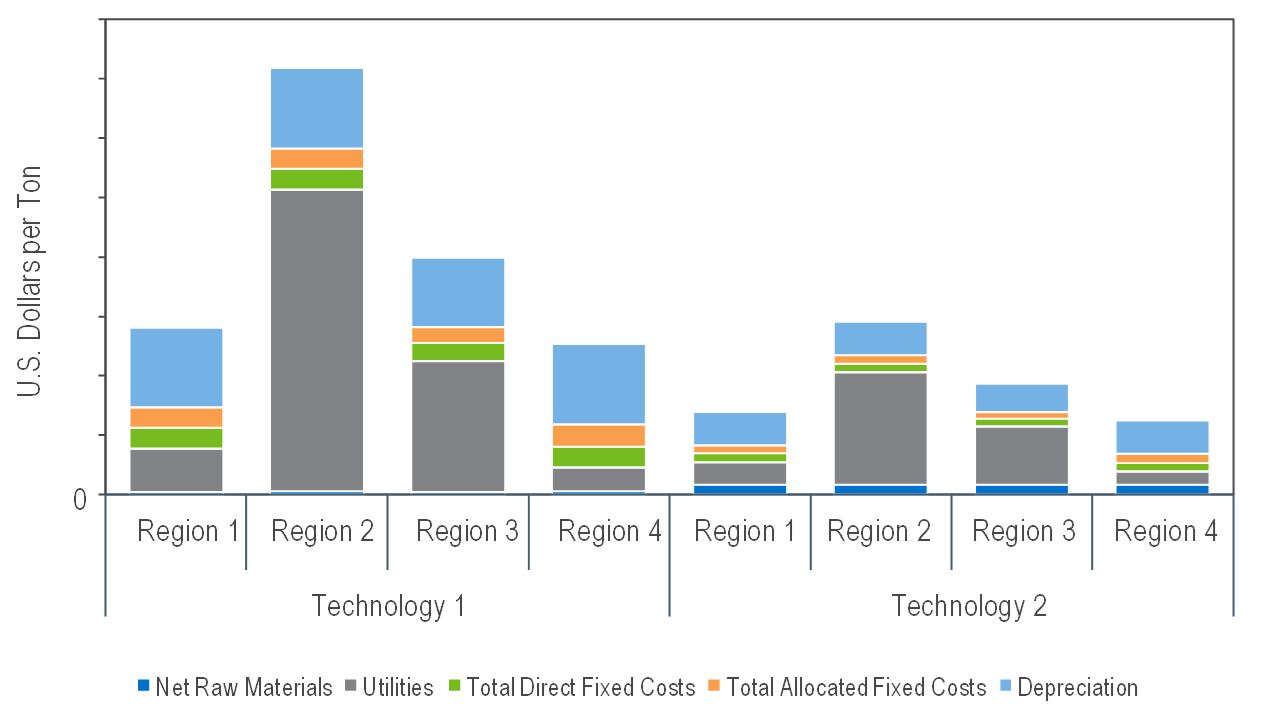
Base-case cost of CO2 capture estimates for sorbent- and solvent-based DAC processes with comparative process economics and comparison for different regions—detailed cost of production estimates are presented for a generic solid sorbent DAC system and a KOH solvent DAC system with a calcium caustic recovery loop for regeneration. Costs are presented in Q1-2023 dollars for the United States Gulf Coast, Western Europe, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East. Sensitivity analysis is also included to consider potential cost reductions from tax credits through the US government’s IRA.
DAC
The Author...
Gabrielle Farrell, Analyst